This paper presents a design scheme of a high-power energy-feedback electric vehicle (EV) charging pile, along with the system’s structure diagram and control principle.
The EV charging pile can achieve fast charging of electric vehicles, and at the same time, use the EV’s battery as an energy storage component to feed electric energy back to the power grid, realizing bidirectional energy flow. The system’s power factor can approach 1, achieving significant energy-saving effects.
System Schematic Diagram
The system has two operating modes: charging mode and EV energy feedback mode. Figure 1 shows the control system structure of the designed EV charging pile operating in both modes. In terms of system principle, it can be divided into two subsystems: a three-level PWM converter and a bidirectional DC-DC converter. It mainly includes four parts: a grid-side filter, a three-level PWM converter, a bidirectional DC-DC converter, and a DC-side filter.
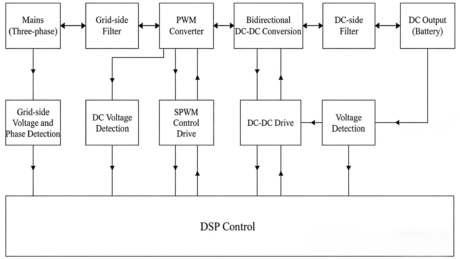
Figure 1. System Structure Block Diagram
The charging pile system designed in this paper mainly includes two operating modes: normal charging mode and EV energy feedback mode. When operating in charging mode, AC/DC conversion is realized through three-phase PFC boost control, converting the AC voltage of the mains power into DC voltage, and the high-voltage DC power is converted into the voltage required for EV charging through the DC-DC converter. When operating in EV energy feedback mode, DC/AC conversion is realized through three-phase PFC constant-voltage inverter control, feeding the energy released by the battery back to the power grid. The bidirectional DC-DC converter completes the conversion between inverted DC energy and battery energy, ensuring the current, voltage, and time control required for the battery charging and discharging process.
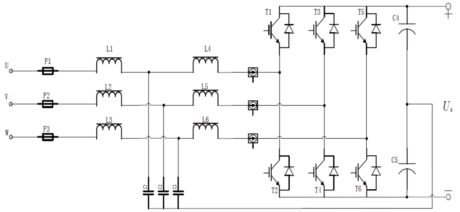
Figure 2. Three-Level PWM Converter
Figure 2 shows the typical voltage-source main circuit structure adopted by the three-level PWM converter. The three-phase mains input is connected to the LC filter (i.e., grid-side filter) through fuses. Its main function is to filter out high-frequency harmonics generated by the three-level PWM converter: first, it improves the input current on the grid side; second, when operating in feedback mode, it makes the three-phase current fed into the grid a pure sine wave, improving the THDi index of the power supply system.
In this design, the grid-side filter has an LCL filter structure, in addition to the traditional L and LC structure filters. Compared with traditional filter structures, the LCL structure filter is a third-order filter in the circuit, which has the advantages of greatly improved harmonic attenuation capability, small space occupation in the actual structure, and the ability to achieve a higher THDi index. Another advantage of using the LCL filter is that it can effectively suppress grid-side harmonic current from pouring into the charging pile system, which helps reduce the current stress of the filter capacitor and improve the stability and reliability of the charging pile system.
To suppress the high-frequency common-mode voltage generated by the converter and improve the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) performance of the power supply system, this design directly connects the neutral point of the Y-connected filter capacitor in the grid-side filter to the neutral point of the DC bus capacitor. Therefore, the grid-side filter in this design is both a differential-mode filter and a common-mode filter, which can effectively filter out the high-frequency common-mode voltage at the switching frequency level generated by the converter.
Figure 3 shows the circuit structure of the bidirectional DC-DC converter, which operates in different ways under the two operating modes of the system.
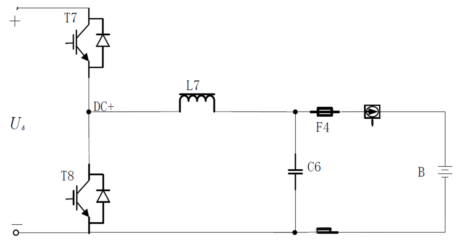
Figure 3. Bidirectional DC-DC Converter
When the system works in charging mode, the DC-DC converter operates in Buck conversion mode. This mode converts the high-voltage constant DC bus voltage into an adjustable DC voltage output through high-frequency step-down, with an output range of 0 V to 600 V. When the system works in EV energy feedback mode, the DC-DC converter operates in Boost conversion mode. This mode converts the DC energy fed back by the EV battery into the designed DC bus voltage through high-frequency step-up, and finally the three-level PWM converter feeds the feedback energy into the power grid. In this design, the bidirectional DC-DC converter adopts a Buck-Boost bidirectional conversion circuit, and the semiconductor switching device adopts the latest generation of IGBT modules. This circuit topology has a simple structure and high reliability, making it the preferred circuit topology for realizing non-isolated bidirectional DC-DC conversion.
